IBM’s Granite large language model (LLM) recently led the BIRD benchmark for handling complex text-to-SQL tasks, signaling major progress in making data insights accessible to all.
The Roadblock: Data Is Plentiful, but Access Isn’t
Businesses collect vast amounts of data, yet most employees struggle to extract value from it without the necessary SQL skills. While SQL remains the standard for database queries, it still requires you to be skilled in SQL to extract value from your data.
Generative AI, particularly LLMs like Granite, are bridging this gap by translating natural language questions directly into SQL empowering a wider audience to tap into organizational data.
Granite’s Edge in Text-to-SQL
IBM’s ExSL+granite-20b-code model, built atop the Granite 20B code foundation, is engineered for translating text into SQL. On the BIRD benchmark, which measures how well AI translates natural language into executable SQL, Granite accurately answers 68% of questions, outperforming other AI solutions but still trailing human engineers. It also scored 80 out of 100 for execution speed, closely approaching the human average of 90, so it’s both quick and effective.
Key Techniques Behind Granite’s Success
- Schema linking: It matches user keywords to relevant tables and columns in the database, quickly narrowing the search.
- Content linking: The model generates SQL snippets that precisely filter and compare data, focusing on accuracy for relevant results.
- SQL generation: By synthesizing the user’s question and schema mapping, Granite produces and selects the optimal SQL query.
This combination of extractive schema-linking and generative content-linking accelerates query production and sharpens accuracy, making Granite both fast and reliable for real-world use.
Enhancing the Data Experience Beyond Queries
IBM isn’t stopping at text-to-SQL, the team is integrating AI-driven tools that enrich data with intuitive descriptions and business-friendly terminology. These features, available in IBM’s Knowledge Catalog and watsonx.data, help users find and understand the data they need without technical barriers.
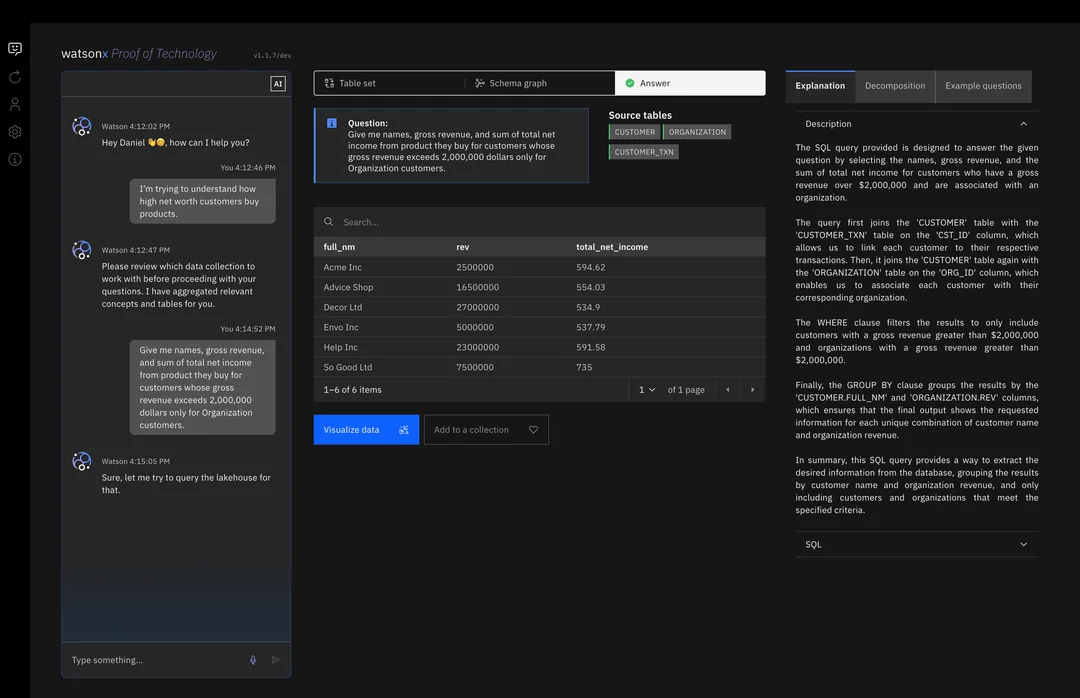
To simplify user interaction further, IBM researchers developed a conversational graphical user interface (CGUI). This chat-based platform allows users to pose questions, view visual data outputs, and even inspect or edit the generated SQL, blending natural language with technical depth.
Conversational GUI Features
- Interactive chat: Users ask questions and receive immediate suggestions and data insights.
- Schema graph: Visual mapping of table relationships helps users navigate unfamiliar datasets.
- Example questions: Built-in prompts inspire users to refine their queries and explore new perspectives.
- Decomposition view: Step-by-step logic and SQL execution details foster transparency and confidence.
- Data visualization: Query results are automatically transformed into editable charts for presentations or reports.
What’s Next for Granite and AI Data Tools?
IBM is collaborating with developers to integrate generative AI capabilities more broadly across the watsonx suite. By continually improving the Granite LLM and its supporting tools, the company aims to match or surpass human performance and user-friendliness, benefitting everyone who relies on data-driven decisions.
Takeaway
IBM’s Granite LLM is transforming how organizations interact with their data. By making complex database queries as simple as a conversation, these AI-powered solutions are set to empower employees of every skill level to uncover insights faster and more efficiently than ever before.
Source: IBM Research Blog

IBM’s Granite LLM Is Maturing Text-to-SQL and Data Access