Imagine solving the toughest medical mysteries faster and more accurately than ever before. This is becoming reality as advanced AI systems are now outperforming even experienced clinicians in diagnosing complex cases while also bringing down healthcare costs.
Benchmarking AI Against Human Experts
The Microsoft AI Diagnostic Orchestrator (MAI-DxO) has redefined diagnostic standards. It achieved an impressive 85% success rate on challenging cases from the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), vastly outpacing the 20% accuracy rate of seasoned physicians. Notably, MAI-DxO also reduces unnecessary tests and expenses, making healthcare more efficient.
- Real-world testing: Microsoft developed the Sequential Diagnosis Benchmark (SD Bench) with 304 intricate NEJM cases, converting each into an interactive, step-by-step diagnostic scenario.
- Broad model evaluation: The platform tested several leading generative AI models including GPT, Llama, Claude, and Gemini, boosting each one’s diagnostic performance.
- Cost simulation: Each action in the diagnostic process carried a virtual cost, accurately reflecting real-world medical spending and resource allocation.
Moving Beyond Multiple-Choice Testing
Traditional benchmarks like the USMLE focus on multiple-choice questions, which primarily test memory. Microsoft’s approach is different: AI must ask questions, order relevant tests, and iteratively refine its diagnoses, mirroring the real clinical decision-making process. This method better captures the complexity of true medical reasoning.
Credit: Microsoft
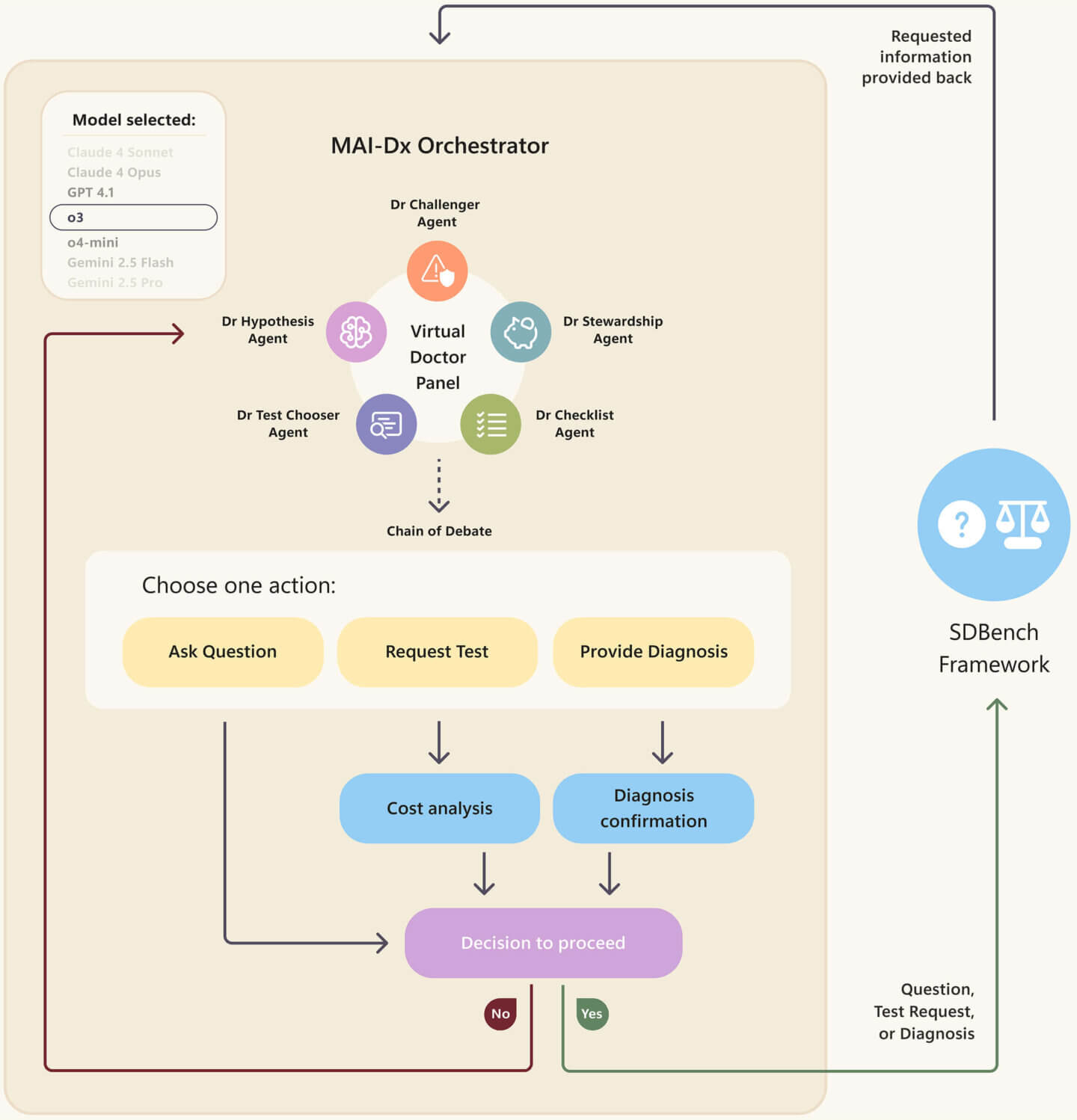
The AI Orchestrator: Simulating a Team of Doctors
MAI-DxO acts as a virtual panel of clinicians, each with distinct diagnostic approaches. As a model-agnostic orchestrator, it integrates multiple AI agents, checks costs, and verifies reasoning before delivering a final diagnosis. This process boosts safety, reliability, and transparency, all vital for clinical settings.
- Higher accuracy and savings: MAI-DxO paired with OpenAI’s o3 model hit 85.5% accuracy, compared to just 20% for practicing doctors.
- Adjustable for balance: The system’s cost settings allow users to balance accuracy with resource expenditure.
- Knowledge synergy: Unlike any single doctor, AI can combine vast breadth and depth of expertise, excelling in rare and complex cases.
What This Means for Healthcare
This breakthrough signals a transformation in healthcare delivery. In the future, patients might manage routine health issues independently, while clinicians tackle complex cases with robust AI-supported tools. MAI-DxO not only boosts diagnostic accuracy but also reduces costs, a major advantage, given that up to 25% of US health spending goes to waste.
However, Microsoft stresses that MAI-DxO is still in the research phase. Broader studies and rigorous clinical validation remain necessary before any real-world implementation. The company is collaborating with healthcare partners to ensure AI solutions are safe, effective, and trustworthy before large-scale use.
Answering Critical Questions
- Is the AI ready for clinics? Not yet further trials and regulatory review are required.
- Will AI replace doctors? No. AI will support, not replace, clinicians - automating routine tasks and enhancing complex decision-making, while doctors remain key for patient trust and empathy.
- Why emphasize cost? Reducing unnecessary testing helps address the widespread problem of over-diagnosis and wasted resources.
- Orchestrator explained: In this context, an orchestrator is a digital conductor, coordinating multiple AI agents for comprehensive and reliable diagnostic reasoning.
The Path Forward
Microsoft’s research marks a significant milestone in the journey toward medical superintelligence. The evidence shows AI can not only match but often exceed human performance in challenging diagnostics. The next phase will focus on real-world validation, ensuring tomorrow’s healthcare combines the compassion of human doctors with the precision of intelligent machines.

AI is Disrupting Medical Diagnostics: Surpassing Human Expertise and Reducing Costs